5 ways to ensure psychological safety for employees
-
 Morgane Oléron
Morgane Oléron

Psychological safety is extremely important because it contributes to employee learning, innovation, and overall satisfaction.
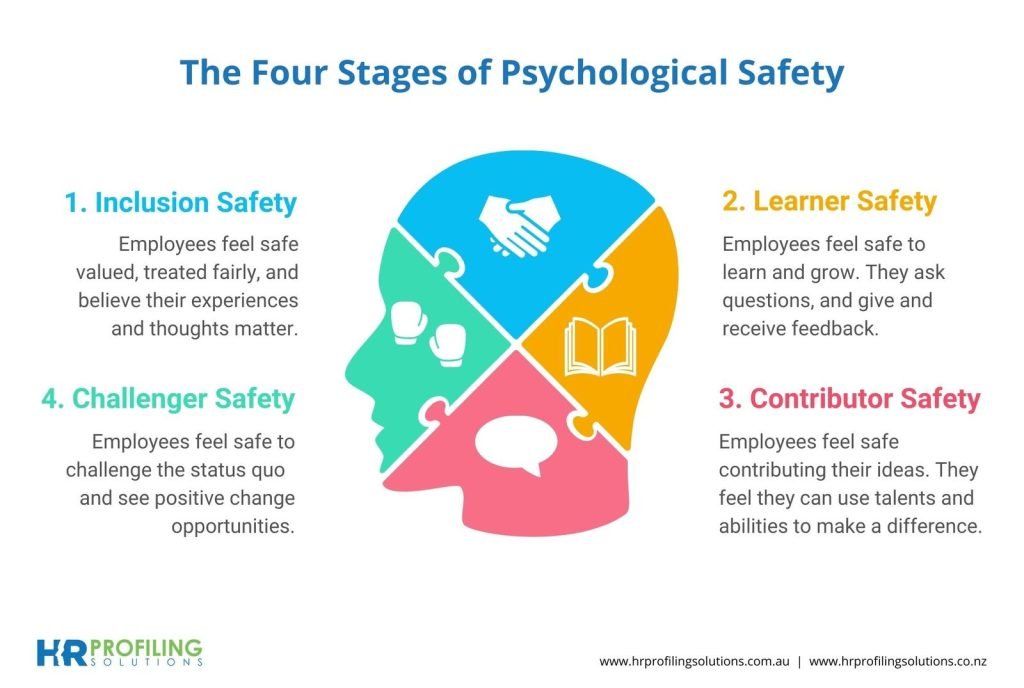
Studies have shown that quality relationships at work play a significant role in ensuring psychological safety and thereby promoting learning processes.
The absence of psychological safety can lead to negative consequences, such as increased tension and conflicts within teams, inefficient work processes, and low employee motivation.
Ultimately, these issues can impair the overall performance and effectiveness of an organization.
Our in-house psychologist, Anastassia Murašina, shares with you five ways you can improve psychological safety in your organization:
1. Promote quality relationships
Quality relationships at the workplace, characterized by mutual respect and a positive attitude, are a crucial foundation for psychological safety. Ensure that employees have the opportunity to build and develop positive relationships with their colleagues.
How to achieve this:
- Organize team-building events that promote communication and collaboration.
- Establish mentorship programs where more experienced employees mentor new hires.
- Provide communication skills training to develop skills for building and maintaining positive relationships.
2. Encourage open communication
Open communication is a key factor in achieving psychological safety. Employees should feel free to express their thoughts and ideas without fear of judgment.

How to do this:
- Create secure communication channels where employees can share their thoughts anonymously or publicly.
- Conduct regular feedback sessions where employees can honestly discuss their concerns and suggestions.
- Train leaders in active listening techniques so they can communicate effectively and empathetically with their teams.
3. Support learning and development

Learning and development are crucial for ensuring employee motivation and satisfaction. A psychologically safe environment encourages employees to participate in learning processes.
How to support this:
- Offer continuing education opportunities and training focused on both technical and social skills.
- Create an inspiring learning environment where failures are seen as learning opportunities rather than punishable mistakes.
- Support the experimentation of new ideas and innovation by providing employees with time and resources to implement their projects.
4. Lead by example

Leaders play a significant role in ensuring psychological safety. Employees follow the behavior of their leaders, so leaders need to demonstrate desired behavioral patterns.
How to do this:
- Leaders should lead by example with open and honest communication.
- Encourage leaders to show vulnerability by acknowledging their mistakes and seeking help, which helps create a trustworthy and open work culture.
- Promote collaborative leadership, where leaders involve employees in decision-making processes and value their contributions.
5. Create a supportive work culture

A work culture that values and supports employee well-being contributes to achieving psychological safety.
How to support this:
- Promote work-life balance by offering flexible working conditions and supporting employees’ personal lives.
- Ensure there are support systems in the workplace, such as counseling services and support groups, where employees can seek assistance.
- Recognize and reward positive behaviors that support collaboration, respect, and mutual support.
Creating psychological safety is an ongoing process that requires attention and dedication.
By implementing these five strategies, you can help create a work environment where employees feel safe, motivated, and ready to learn and grow.
Additionally, it is important to engage external specialists, such as psychologists, organizational psychologists, and coaches, who can provide an unbiased perspective and help the organization move in the desired direction.
Want to know more about how Siffi is helping organisations? Check out our services
About the author

Morgane Oléron
Psychology Content Writer at Siffi
Morgane crafts compassionate, engaging content that makes mental health conversations more human and accessible. At Siffi, she combines storytelling with strategy to foster a culture of care and connection in the workplace.
Recent Posts
-
How to handle giving and receiving feedback during yearly performance interviews12 Jan 2026
-
What HR should really get from their wellbeing platform15 Dec 2025
-
From burnout to belonging: How mental health platforms reduce avoidable turnover08 Dec 2025
-
Comparing the top 6 digital mental health platforms for workplace wellbeing01 Dec 2025
Newsletter
Sign up for our newsletter and get monthly tips and tricks for better mental well-being from our certified therapists and coaches.